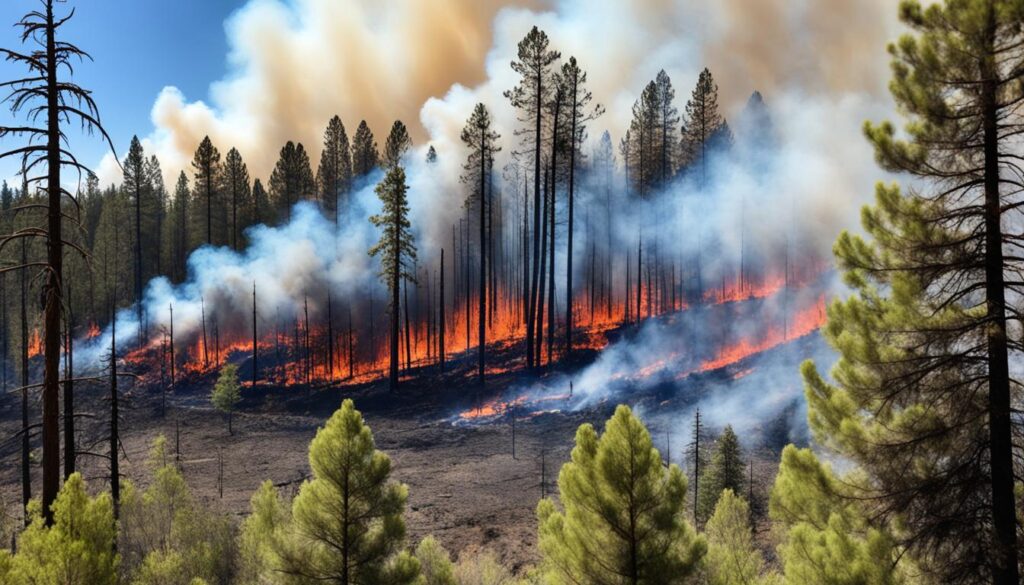
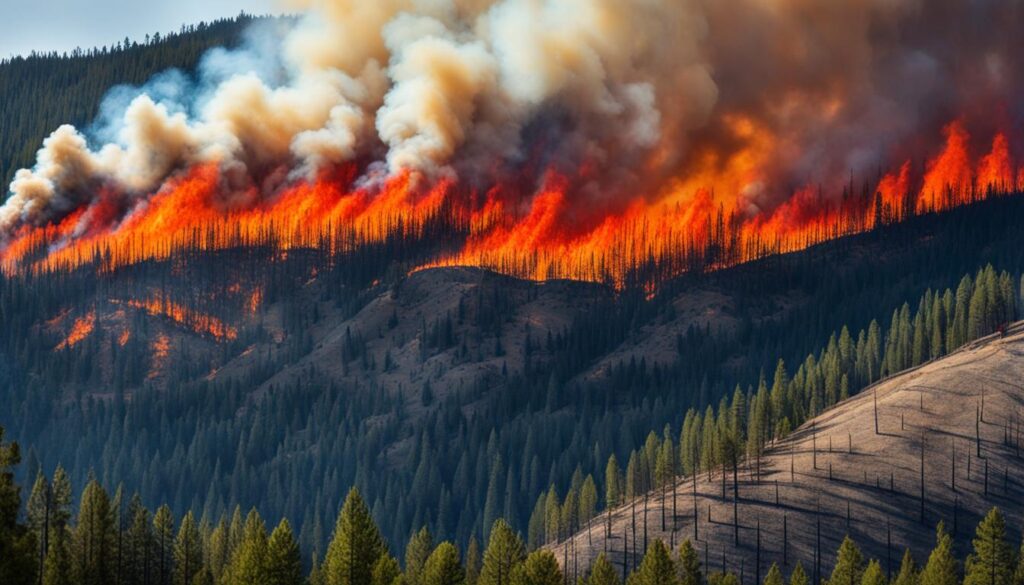
Every year in the U.S., over 73,000 wildfires burn about 7 million acres. This shows how powerful nature can be. It highlights the need to understand Wildland Fire Behavior and Ecology and its effects on wildland fire management. Knowing how wildfires spread is key to keeping people and nature safe.
Firefighters get better with research on fire behavior. This helps make them safer and more effective. Tools like BehavePlus and FlamMap are key. They help predict fire behavior and guide how to fight fires.
The National Fire Danger Rating System links research with action. It helps fire managers predict fire threats. This system is crucial for keeping people and nature safe from fires.
Wildfires are complex. They can hurt the environment but also help it by making habitats better. By studying how fires have changed landscapes, we learn how to live with them.
In some forests, fires help new trees grow. In others, they deal with the effects of past fires. These stories teach us how to adapt to fires.
Fire can destroy and also help ecosystems. Understanding wildfires helps us protect firefighters and nature. It’s a big challenge but also an important one.
The Critical Role of Fire Behavior Research in Wildland Management
Fire behavior research is key to understanding and managing wildland fires. It helps predict and lessen the effects of these disasters. This is vital for protecting people and property and making ecosystems more resilient to wildfires.
Advancements in Fire Behavior Modeling and Simulation
Recent work in fire behavior modeling has greatly improved how we simulate fires. Now, models use better data on fuel moisture, wind, and land shape. This makes predicting fire spread more accurate. These tools are now crucial for planning how to fight fires.
Fuel Moisture Effects on Fire Dynamics
Fuel moisture, like live fuel moisture content (LFMC), is very important for fire behavior. It affects how intense and fast fires spread. Studies show that different moisture levels in plants change how fires behave in different places.
Increasing Ecosystem Resilience through Fire Behavior Understanding
Knowing about fire behavior helps make ecosystems more resilient to wildfires. By understanding how fires affect different ecosystems, we can plan better. This means not just fighting fires but also helping the land recover after fires.
Wildfires are becoming a bigger problem due to climate change and human actions. Fire behavior research is more important than ever. It helps us use better tools and models to protect people and nature. The knowledge from this research helps make policies that support sustainability and resilience against fires.
Wildland Fire Behavior and Ecology: Interplay of Fuels, Topography, and Weather
Understanding wildfire behavior patterns is complex. It involves fuels, topography, and weather. Fire ecology research shows these elements work together. They affect how fires start, spread, and stop.
Topography greatly impacts wildland firefighting. It controls where and how fires spread. Fires act differently on north and south slopes. North slopes are cooler and wetter, slowing fires. South slopes get more sun, making them more prone to fires.
The steepness of a slope affects fire movement. Fires move faster on steep slopes. This is because heat warms the ground fuels, making them burn faster.
This shows topography changes how we fight fires. Here’s how topography affects wildfires:
- Sun exposure: South slopes get more sun, so they have less moisture.
- Slope gradient: Steeper slopes make fires move faster, thanks to wind and heat.
- Aspect: North and south slopes have different temperatures and humidity, affecting fuels.
Climate change affects fire behavior too. Warmer temperatures and changing rain make fires more likely. This changes when fires happen and how they behave. Fuel types and wildfire spread also matter. The materials that can burn decide how fires start and spread. These materials are influenced by topography and weather.
Knowing about topography helps fire experts and firefighters. It lets them plan better, saving land from fires. Research aims to improve predictions and fire management.
Conclusion
Understanding wildfire patterns is key to better fire management. E. Louise Loudermilk, Joseph J. O’Brien, and their team showed us how important it is. Their 2022 study in Fire Ecology helps us get wildland fire behavior.
They found that vegetation, weather, and land shape fire behavior. This research is based on how fires work and their effects. It tells us that knowing about these things is crucial.
Natural fires helped shape many ecosystems, especially in North American forests. Many trees still show signs of past fires. This shows that fires were a normal part of the environment long ago.
The Forest Service now focuses more on managing fires and fuels. This change is like what Harold Weaver suggested over 70 years ago. He believed in letting fires happen naturally to help ecosystems.
Now, we need to understand fire behavior and natural fire processes to keep communities safe and ecosystems healthy. By using new fire behavior models, we can make policies that protect both nature and people. The right strategies can save homes and lives, as seen in western Montana in 2000.
So, we must use science and practice to manage wildland fires better. This way, we can live with nature’s power without getting hurt.